Two space agencies say we need filter systems for drinking moon water, and they need the public’s help with the AquaLunar challenge.
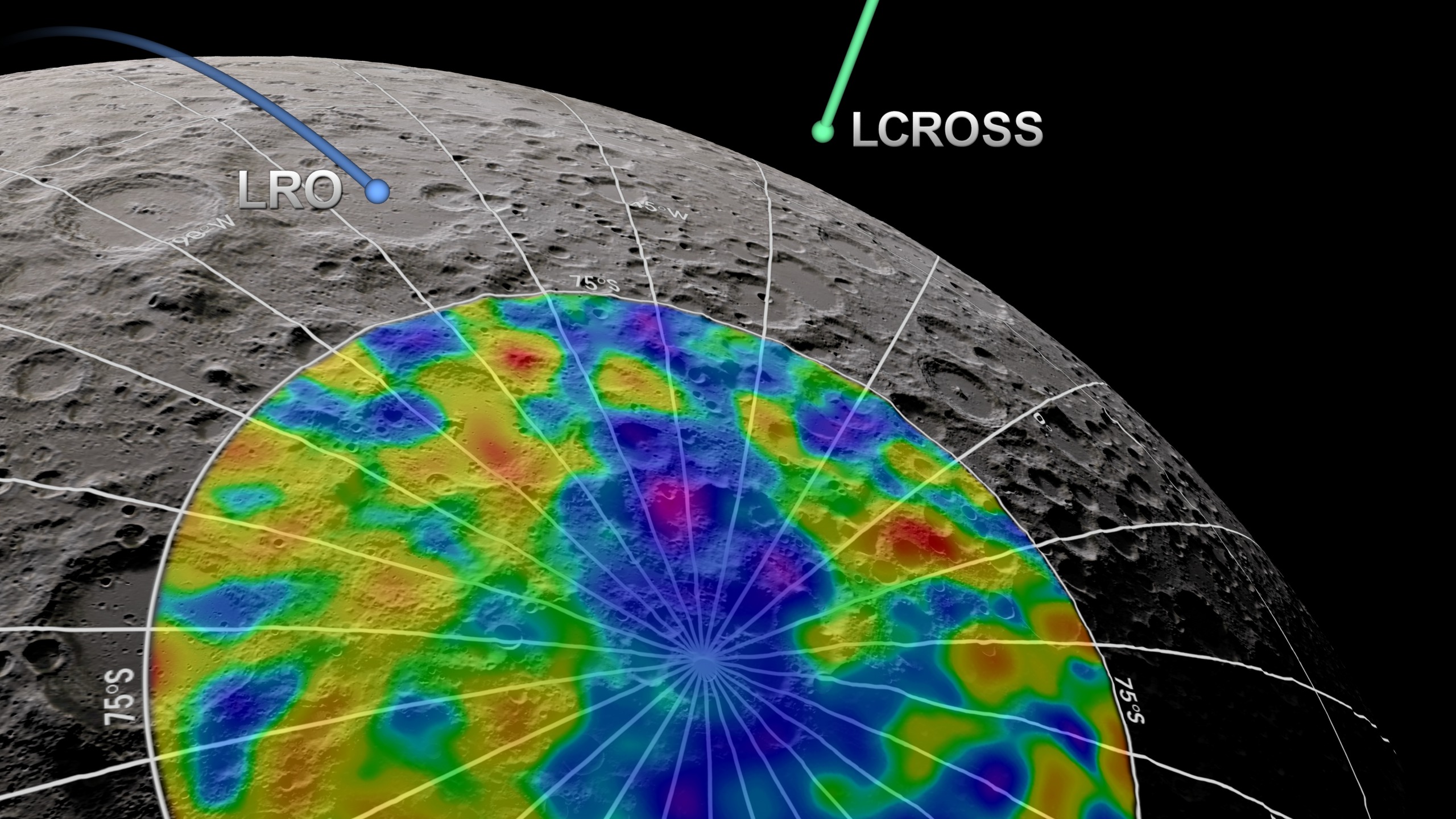
Artist’s illustration of hydrogen concentrations at the moon’s south pole; hydrogen is an indicator of water. Above are two NASA spacecraft: LCROSS, which deliberately impacted the moon in 2009, and the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, which tracked the composition of the plume LCROSS generated. (Image credit: NASA/Goddard Space Flight Center Scientific Visualization Studio)
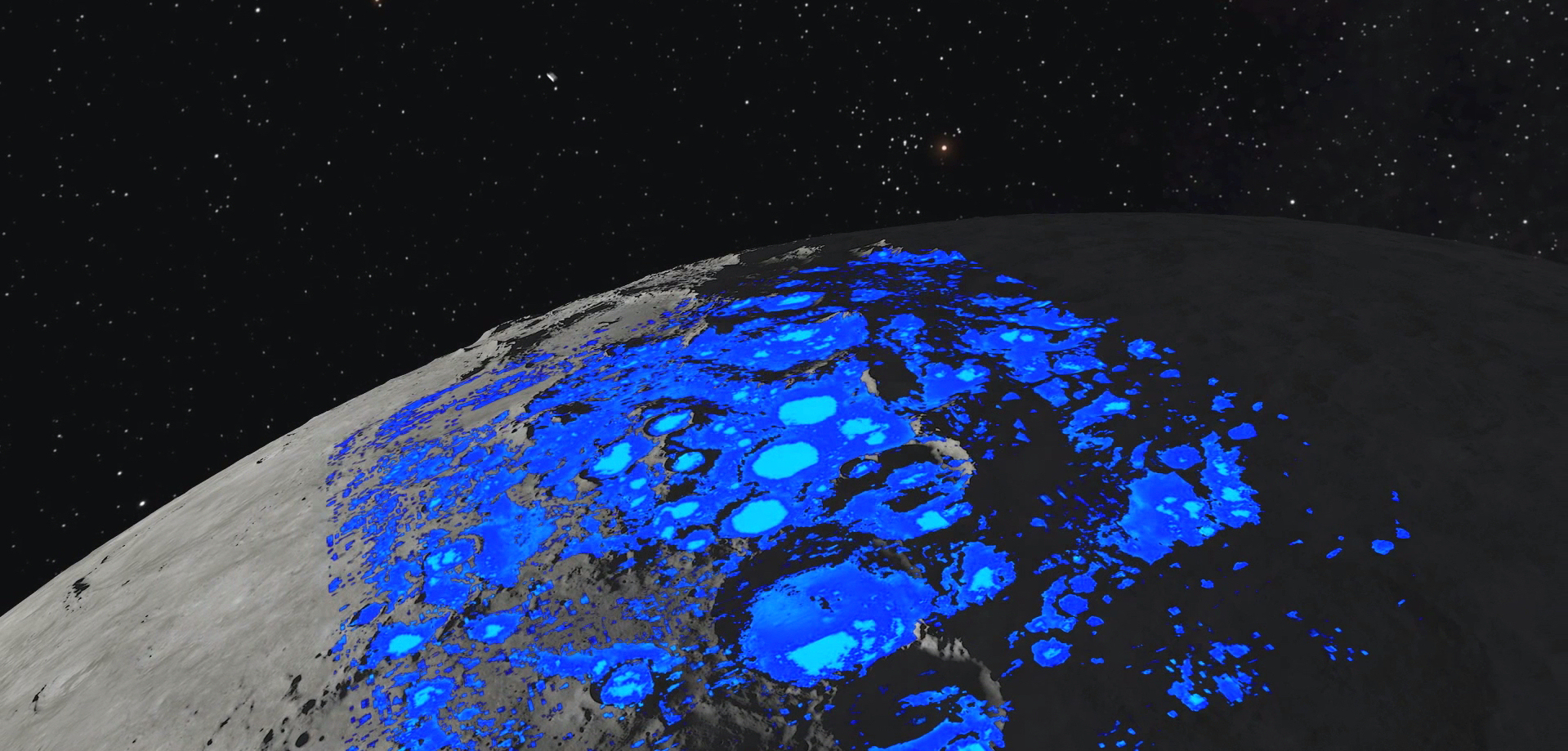
Water appears to be abundant near the moon’s south pole, but drinking it could be a safety problem for astronauts.
A new moon challenge asks the public for ideas to purify drinking water for astronauts, reducing the need for shipments from Earth. The Aqualunar contest is open to residents of Canada and the United Kingdom, and you can send in your ideas right now, through April 8.

“It is very likely that water exists on the moon, but it contains contaminants,” the Canadian Space Agency wrote in its briefing for participants. That statement is based on data from a deliberate crash of a NASA spacecraft, LCROSS, into the icy south polar region of the moon on Oct. 9, 2009.
The resulting plume from LCROSS (short for “Lunar Crater Observation and Sensing Satellite”) not only contained the hydrogen expected from water, but also featured carbon monoxide, calcium, mercury and magnesium, according to a 2010 Science paper about the discovery led by researcher at NASA’s Ames Research Center in California.
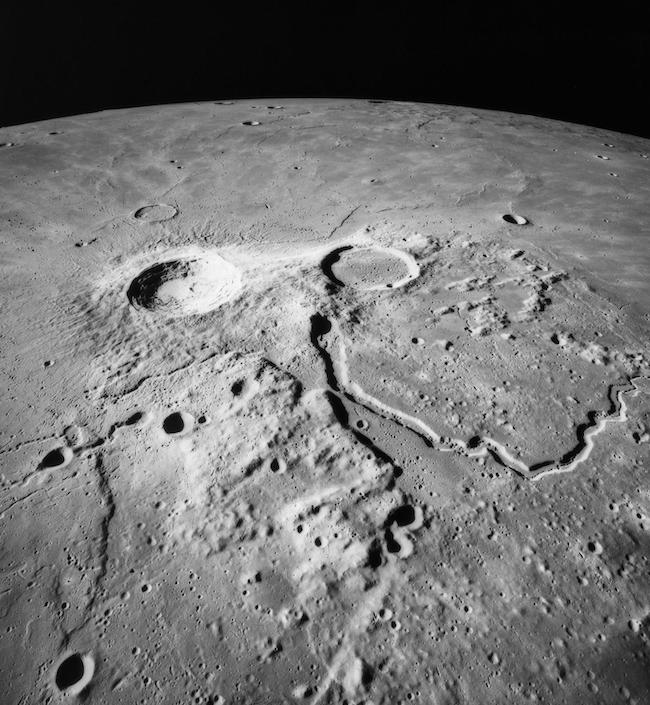

Magnesium and calcium are commonly found in “hard water,” but mercury is a highly toxic substance. As such, contaminants like it cannot be consumed by astronauts with the NASA-led Artemis program, who are expected to touch down at the south pole later in the 2020s.

“Lunar purification of in-situ water has never been demonstrated successfully on the lunar surface, and there are multiple challenges that exist in a space-based environment,” CSA officials stated in the Canadian guidelines. While space solutions commonly help remote communities on Earth (a priority of CSA’s mandate), the technology that exists today is not as beneficial, the agency noted.
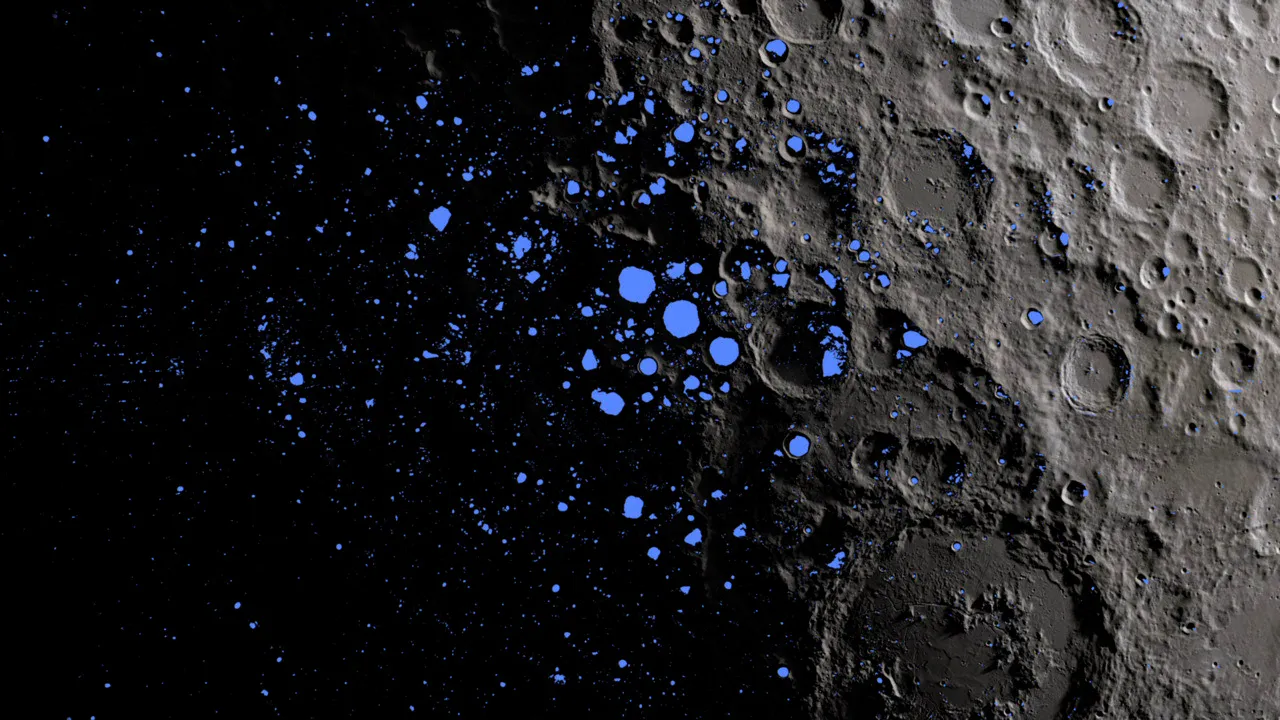

The south pole of the moon likely has a lot of water, but it’s far from pure. (Image credit: NASA)
Issues the challenge participants will face in their designs include the highly corrosive lunar soil (or regolith), the need to ship low-mass systems to the moon due to rocket lifting constraints, and the requirement to operate in only one-sixth of Earth’s gravity on the moon’s surface, among other problems, the CSA added.
The U.K. Space Agency’s guidelines for participants additionally outline a number of contaminants participants will need to account for, including hydrogen sulfide, ammonia, carbon monoxide, ethylene, sulfur dioxide, methanol and methane, along with “traces of solid regolith.”

The solutions are expected to benefit numerous audiences, the U.K. Space Agency wrote in a press release, including “removing microplastics from the oceans [and] providing clean drinking water in low-income countries and drought-prone areas.”
Each country has its own judging process, funding and eligibility, and more details for participants in each country are available at the respective websites linked above. Generally speaking, participants will be expected to submit a concept design by April 8. If selected for further stages, teams will next submit proofs of concept and prototypes in new rounds, with the grand prize in each country announced in 2026.