Two gargantuan structures discovered near our galaxy’s ancient heart may be some of the earliest building blocks of the Milky Way. Researchers have named them Shiva and Shakti.
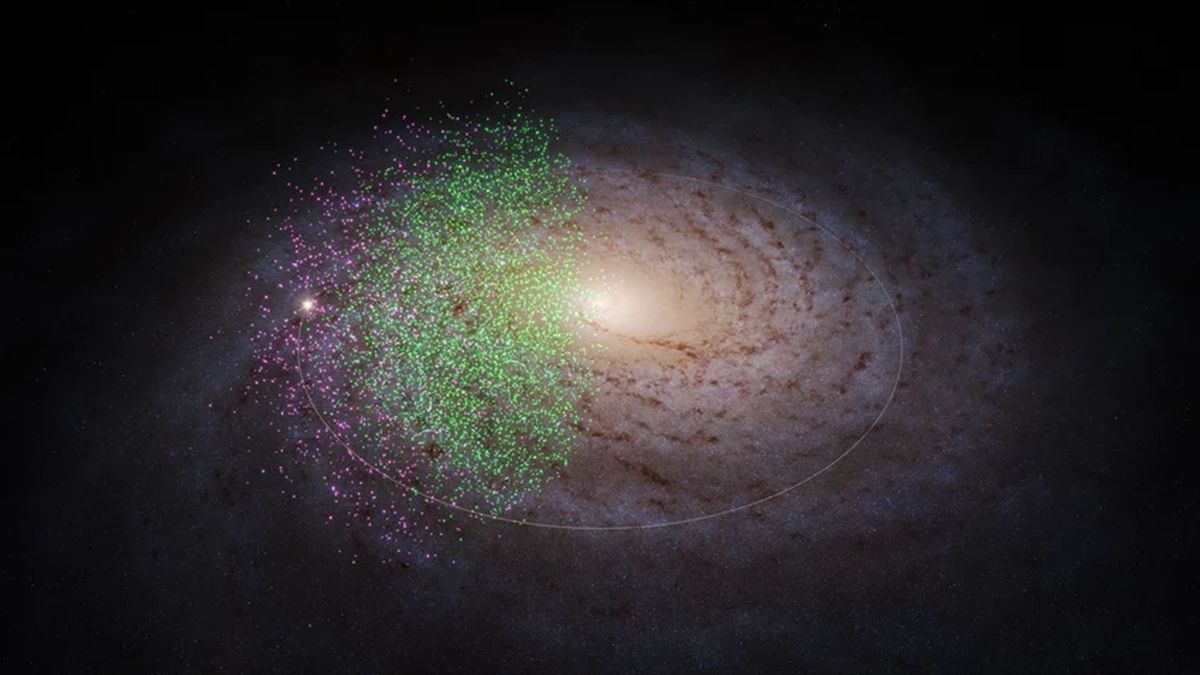
Two gargantuan streams of stars named Shiva (shown in green) and Shakti (purple) may be some of the oldest building blocks of the Milky Way galaxy. (Image credit: © S. Payne-Wardenaar / K. Malhan / MPIA)
Astronomers peering into the heart of the Milky Way have discovered two gargantuan, never-before-seen structures. These vast “streams” of stars each contain the mass of 10 million suns and are up to 13 billion years old. They span wide swathes of the galaxy and may be some of the earliest building blocks of our Milky Way, scientists with the Max Planck Institute for Astronomy (MPIA) said.

The two structures — described in a new study published March 21 in The Astrophysical Journal — have been named Shiva and Shakti, after the divine Hindu couple whose union is said to have brought harmony to the universe. The newfound stellar streams appear to have merged with the early Milky Way between 12 billion and 13 billion years ago, fueling our galaxy’s growth.

“What’s truly amazing is that we can detect these ancient structures at all,” lead study author Khyati Malhan, an astrophysicist at MPIA said in a statement. “The Milky Way has changed so significantly since these stars were born that we wouldn’t expect to recognise them so clearly as a group.”

The researchers spotted the cosmic structures using the European Space Agency’s Gaia space telescope — a floating observatory that’s been mapping the shape and structure of the Milky Way since 2014. By charting the speed, position and motion of more than 1.5 billion stars in our galaxy, Gaia’s observations enable astronomers to draw connections between groups of stars that share similar origins, helping to piece together our galaxy’s history.

It’s thought that the Milky Way has collided with neighboring galaxies at least a dozen times over the last 12 billion years, with each merger funneling fresh stars into our evolving galaxy. The Gaia telescope has helped reveal several of these collisions — including a previously unknown merger with the so-called Gaia sausage dwarf galaxy, which our insatiable Milky Way swallowed 10 billion years ago, giving our galaxy its bulging center.

The team’s analysis showed that Shakti’s stars orbit further from the galactic center and in a more circular orbit than Shiva’s — but both structures contain stars that are extremely metal poor, meaning they lack the heavier elements forged through stellar fusion later in the universe’s history. This means Shiva and Shakti likely contain some of the oldest stars in the Milky Way, making the newfound streams some of the first building blocks upon which the galaxy evolved.

To better understand how Shiva and Shakti’s union with the Milky Way contributed to the current state of our galaxy, the team will continue studying them through several ongoing sky surveys. Sadly, there is a strict deadline for this research: In about 4.5 billion years, the Milky Way’s next big collision will unfold as the nearby Andromeda galaxy merges with ours. Whatever life exists on our planet then will have a completely different view of the night sky than we do today.